I'm always excited to take on new projects and collaborate with innovative minds.
+855 12 282 686
samnangrosady9@gmail.com
I'm always excited to take on new projects and collaborate with innovative minds.
+855 12 282 686
samnangrosady9@gmail.com
GitLab CI/CD Auto-Pull is a technique that allows your remote server to automatically pull the latest code changes whenever updates are pushed to a GitLab repository. This eliminates the need for manual intervention in deployments, making the process seamless and efficient.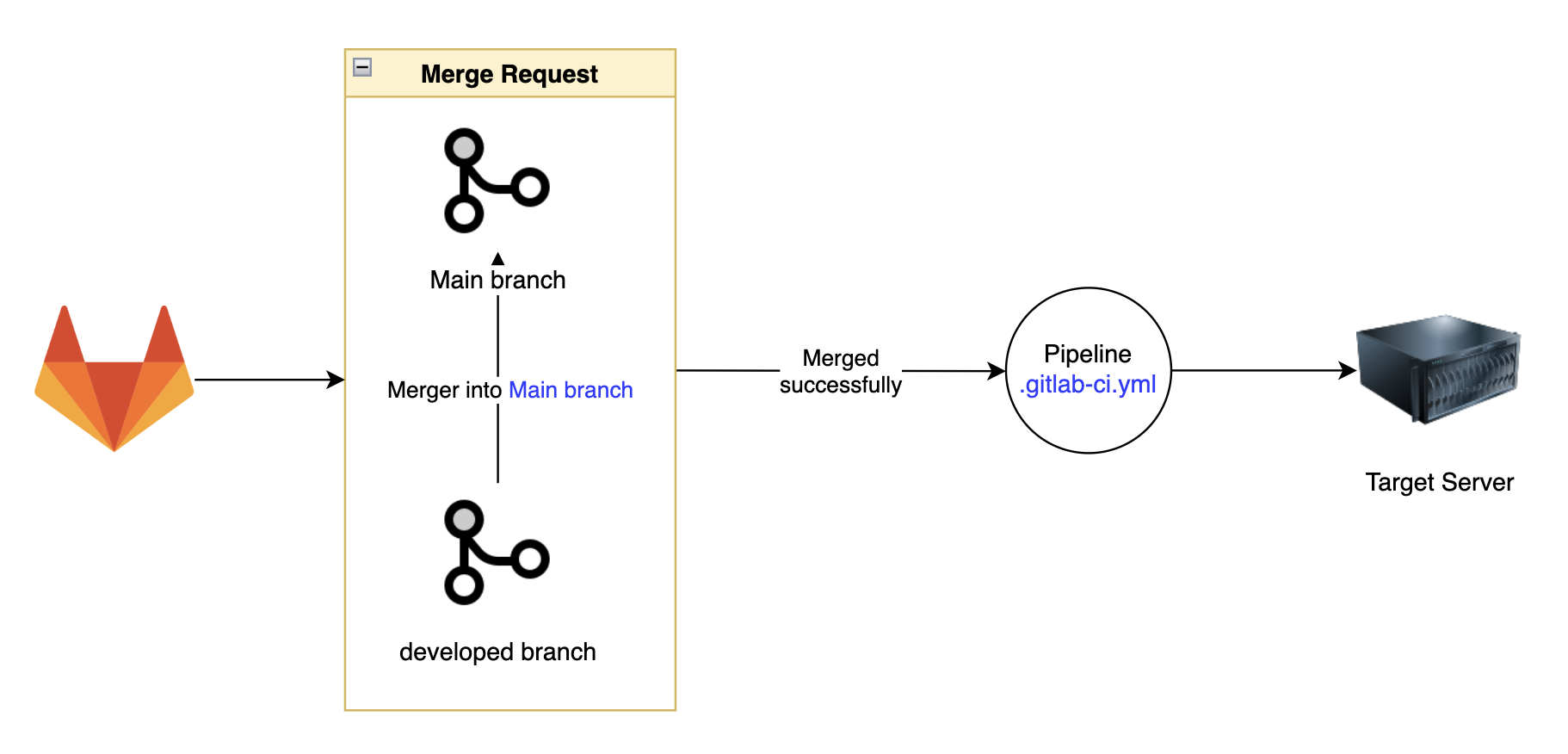
Manually logging into a server and pulling new code updates can be tedious and error-prone. Automating this process offers several benefits:
How to get openssh-private-key
Test SSH Access
ssh <linux-user>@<PRODUCTION_IP>
Get openssh-private-key
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no ssh <linux-user>@<PRODUCTION_IP> "cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa"
Value should be:
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
....
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
Go to GitLab Project → Settings → CI/CD → Variables You can add credential variable there. For example: openssh-private-key (PROD_SSH_PRIVATE_KEY).
PROD_SSH_PRIVATE_KEY: Should openssh-private-key of <linux-user> which accessable to project directory, should not be root user.
Key: PROD_SSH_PRIVATE_KEY
Value: <openssh-private-key>
Type: Variable
Environment scope: All (default)
Protect variable: Checked
Mask variable: Checked
.gitlab-ci.ymlGo to GitLab Project → Build → Pipeline editor
variables:
DOCKER_HOST: tcp://docker:2375
SSH_USER: <linux-user>
PRODUCTION_IP: <server-ip: xx.xx.xx.xx>
services:
- docker:dind
stages:
- deploy_production
deploy-prod:
stage: deploy_production
image: alpine:latest
before_script:
- apk add openssh-client openssh
- eval $(ssh-agent -s)
- echo "$PROD_SSH_PRIVATE_KEY" | tr -d '\r' | ssh-add -
- mkdir -p ~/.ssh
- chmod 700 ~/.ssh
script:
- echo -e "This CI job deploys Stage= [$CI_JOB_STAGE], Branch= [$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH], Server IP= [$PRODUCTION_IP]"
- ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no ${SSH_USER}@${PRODUCTION_IP} -p 22 "cd <project-path> && git pull origin <branch>"
- echo -e "\033[0;32mPulled [$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH] \033[0m"
rules:
- if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "<branch>"'
when: manual
Full content:Dev.to